X-Road is a centrally managed distributed data exchange layer between information systems that provides a standardized and secure way to produce and consume services.
X-Road implements a set of standard features to support and facilitate data exchange and ensures confidentiality, integrity, and interoperability between data exchange parties:
address management
message routing
access rights management
organization-level authentication
machine-level authentication
transport-level encryption
time-stamping
digital signature of messages
logging
error handling.
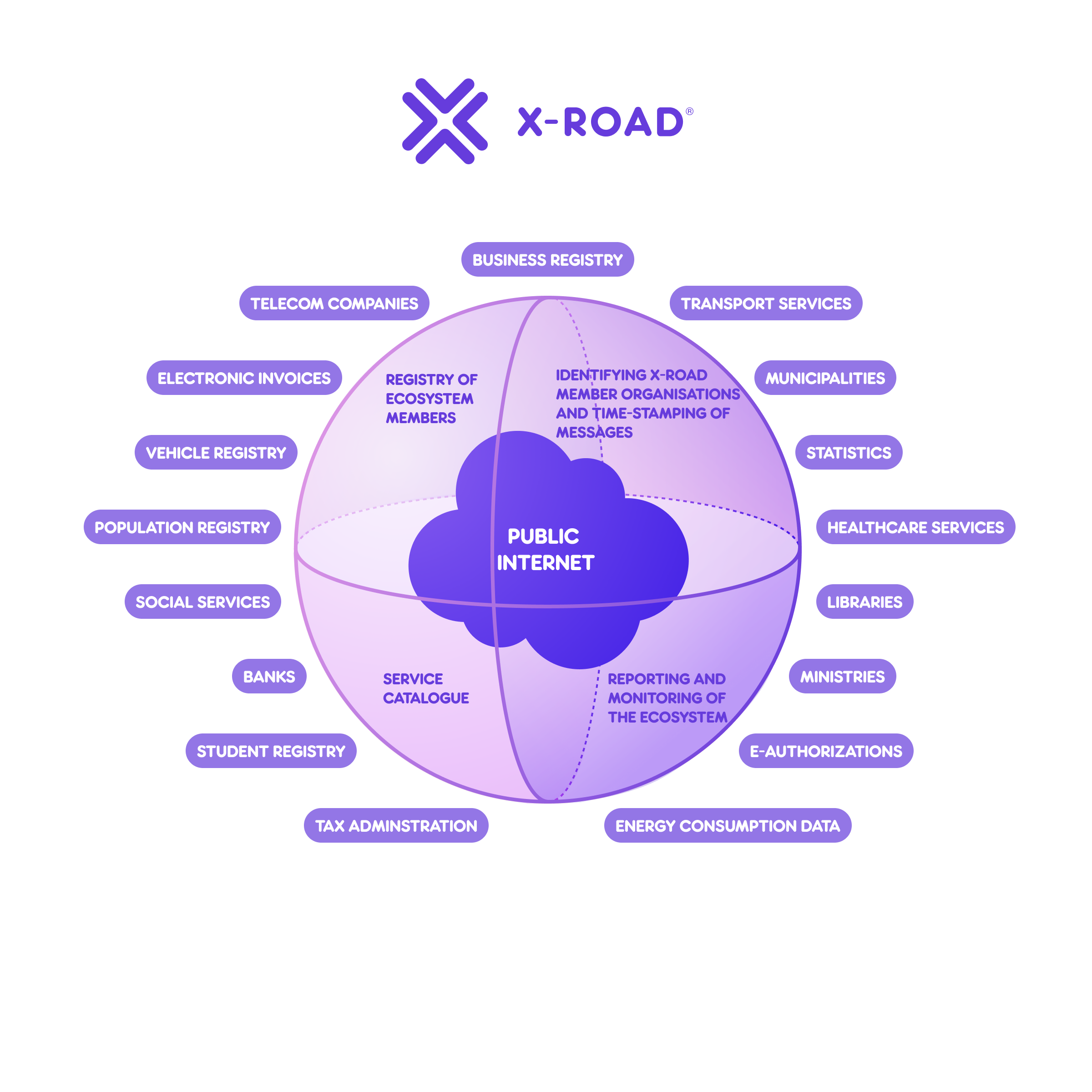
X-Road Ecosystem
An X-Road ecosystem is a community of organizations using the same instance of the X-Road software for producing and consuming services. The owner of the ecosystem, the X-Road Operator, controls who are allowed to join the community, and the owner defines regulations and practices that the ecosystem must follow.
The ecosystem may be nationwide, or it may be limited to organizations meeting specific criteria, e.g., clients of a commercial service provider. Technically, the X-Road software does not set any limitations to the size of the ecosystem or the member organizations.
Trusted Network
Even if X-Road software is open-source, joining an X-Road ecosystem requires going through an onboarding process. During the process, the identity of each organization and technical access point is verified using certificates that are issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA). The identities are maintained centrally, but all the data is exchanged directly between a service consumer and a service provider.
Message routing is based on organization and service level identifiers that are mapped to physical network locations of the services by X-Road. All the evidence regarding the data exchange is stored locally by the data exchange parties, and no third parties have access to the data. Time-stamping and digital signature together guarantee non-repudiation of the data sent via X-Road. The logs provided by X-Road can be used in a court proceeding as evidence.
Authorization Framework
X-Road implements an authorization framework that is used to manage access rights to services. Access rights management is based on the organization and service level identifiers.
The key idea of X-Road is that each service provider owns its data and is responsible for managing access rights of its services. In other words, publishing service to X-Road does not mean that the service is automatically accessible to all X-Road member organizations. Usually, access rights are granted on the information system level – a service provider grants a specific information system access to a service.
Monitoring and Reporting
X-Road provides monitoring and reporting capabilities that can be used to collect operational reporting data and technical monitoring information from the ecosystem. The information can be used to measure the usage of individual services, understand dependencies and relationships between different information systems and services, monitor service health, monitor used X-Road software versions, etc. Each X-Road member organization can access its own data, whereas the X-Road operator can access all the members’ data.
Cross-border Data Exchange
X-Road provides built-in support for cross-border data exchange through federation, which means joining together two X-Road ecosystems. Members of the federated ecosystems can publish and consume services with each other as if they were members of the same ecosystem.
It is possible to create federation connections with multiple ecosystems, but transitive federation relationships are not supported. An ecosystem does not have a federation relationship with another ecosystem that it's not directly federated with.



-3333AB?logo=data:image/svg%2bxml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMzEiIGhlaWdodD0iMzMiIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAzMSAzMyIgZmlsbD0ibm9uZSIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIj4KPHBhdGggZD0iTTE0LjIwMDggMjEuMzY3OEwxMC4xNzM2IDE4LjAxMjRMMTEuNTIxOSAxNi40MDAzTDEzLjk5MjggMTguNDU5TDE5LjYyNjkgMTIuMjExMUwyMS4xOTA5IDEzLjYxNkwxNC4yMDA4IDIxLjM2NzhaTTI0LjYyNDEgOS4zNTEyN0wyNC44MDcxIDMuMDcyOTdMMTguODgxIDUuMTg2NjJMMTUuMzMxNCAtMi4zMzA4MmUtMDVMMTEuNzgyMSA1LjE4NjYyTDUuODU2MDEgMy4wNzI5N0w2LjAzOTA2IDkuMzUxMjdMMCAxMS4xMTc3TDMuODQ1MjEgMTYuMDg5NUwwIDIxLjA2MTJMNi4wMzkwNiAyMi44Mjc3TDUuODU2MDEgMjkuMTA2TDExLjc4MjEgMjYuOTkyM0wxNS4zMzE0IDMyLjE3OUwxOC44ODEgMjYuOTkyM0wyNC44MDcxIDI5LjEwNkwyNC42MjQxIDIyLjgyNzdMMzAuNjYzMSAyMS4wNjEyTDI2LjgxNzYgMTYuMDg5NUwzMC42NjMxIDExLjExNzdMMjQuNjI0MSA5LjM1MTI3WiIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiLz4KPC9zdmc+Cg==)